Deepfakes are Digital Gold
Deepfakes are beneficial allies. Despite the controversy sparked by deepfake misuse, the capacity to create convincing AI-generated simulations generally holds positive prospects for humanity. Deepfakes, AI-crafted hyperrealistic fabrications, have garnered notoriety as potential vehicles of disinformation and deceit. Yet, these very innovations hold the promise of beneficial and even revolutionary uses in the commercial realm.
Throughout history, technological advancements have often been a double-edged sword. The internet, for instance, revolutionised communication and information access, yet it also paved the way for cybercrime and hacking. Similarly, while aeroplanes have made global travel a reality, they have also been used for wartime bombings. This pattern holds true for nearly every innovation: their potential for misuse accompanies their benefits. The crux lies not in the technology itself, but in the social systems and regulatory frameworks governing its use. It’s crucial to focus on how society manages and regulates these technologies rather than blaming the technology itself. Responsible governance and ethical oversight are key to ensuring technological advances serve the greater good, minimising misuse while maximising benefits. With the right safeguards in place, Deepfakes or Synthetic Media (their official name) will be a force for good.
The range of deepfake applications is expanding in positive directions. They’re being used for purposes like reviving historical figures in museums and facilitating video editing without reshoots. Deepfake technology enables us to recreate or imagine things that either no longer exist or have never existed. Beyond entertainment and education, it’s finding increasing utility in medicine and other fields.
Deepfakes refer to highly realistic, AI-generated content, usually in the form of images, videos, or audio, that convincingly replace the likeness of one person with another. The term “deepfake” is a combination of “deep learning” and “fake,” reflecting the use of deep neural networks in creating this synthetic content.
Deep learning techniques, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), are often employed in the creation of deepfakes. GANs consist of two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—that work together to produce increasingly realistic content. The generator creates synthetic content, and the discriminator evaluates its realism. This iterative process continues until the generated content is indistinguishable from authentic material.
Initially, deepfakes gained attention for their ability to superimpose one person’s face onto another in video footage, creating realistic but fabricated scenarios. While deepfakes have been used for entertainment purposes, such as inserting actors into famous movie scenes, they have also raised concerns due to their potential for misuse, including spreading misinformation, impersonation, and privacy violations.

Deepfake technology has evolved beyond face-swapping and now encompasses voice synthesis and the generation of entirely fabricated images, making it a versatile tool with both positive and negative implications. It has applications in various fields:
- Entertainment Industry:
One of the most evident advantages of deepfakes lies in their potential to revolutionise the entertainment industry. Technology allows filmmakers to recreate historical events, bring deceased actors back to the screen, and seamlessly blend fiction with reality. This opens new avenues for storytelling and offers audiences a unique and immersive cinematic experience. A novice artist, with little technical expertise, can use deepfake tools to create a compelling music video featuring their favourite artists. This democratisation of content creation empowers individuals to produce high-quality projects without advanced skills.
For Example: A film where actors from different eras collaborate seamlessly, bringing together legends like Audrey Hepburn and Tom Hanks in a single cinematic experience. Deepfake technology can make this cross-generational storytelling a reality.
Musicians can create virtual concerts featuring collaborations between living and historical artists, offering audiences a unique and immersive audiovisual experience.

Another example is, a deepfake of actor Bill Hader seamlessly transitioning into impressions of various celebrities during an interview went viral, showcasing the entertainment potential of the technology.
Filmmakers can also use deepfake technology to recreate historical figures with a high degree of accuracy, making historical documentaries more engaging. Picture a documentary about World War II where leaders like Winston Churchill deliver speeches in a remarkably authentic manner, providing a vivid and relatable connection to history.
- Historical and Cultural Preservation:
Preserving and reviving historical and cultural artefacts is a challenging task. Deepfakes can contribute to this effort by bringing historical figures and events to life with a level of realism previously unimaginable. Museums, educational institutions, and cultural organisations can use this technology to breathe new life into exhibits, making history more accessible and engaging for the public.
For Example: Museums can revitalise historical exhibits by using deepfakes to recreate key moments with astonishing realism. Imagine standing next to a lifelike version of Abraham Lincoln, delivering the Gettysburg Address.

- Empowering Digital Avatars and Virtual Assistants:
Deepfake technology can play a pivotal role in enhancing digital avatars and virtual assistants. By imbuing these virtual entities with more realistic facial expressions, gestures, and voice modulation, users can experience more natural and engaging interactions. This advancement could revolutionise customer service, making interactions with virtual assistants more intuitive and enjoyable.
Deepfakes can contribute to the evolution of digital interfaces, making technology an even more integral part of our daily lives.

For Example: Virtual assistants equipped with deepfake technology could not only understand spoken commands but also convey empathy through realistic facial expressions. This could revolutionise customer service interactions, making them more human-like and enjoyable.
- Deepfake Voice Technology: Companies in the tech industry have developed deepfake voice technology. There are instances where AI-generated voices closely mimic real voices, potentially for use in virtual assistants or voiceovers. Adobe, for example, showcased a tool called Project Voco that could generate realistic-sounding speech.
- Personalized Learning and Communication:
In the realm of online education and communication, deepfakes have the potential to enhance personalization. Educators can use technology to create tailored learning materials, adapting content to individual learning styles. Similarly, in video conferencing and communication tools, deepfakes can be employed to refine virtual interactions, making them more engaging and personalised.
Deepfakes offers an exciting avenue for transforming the way we connect and learn in the digital age.

For Example: Online educators can create custom-tailored lessons using deepfake technology, adapting content to individual learning styles. Imagine a language learning app where virtual tutors engage learners in realistic conversations, providing a dynamic and personalised learning experience.
Medical students can engage in lifelike surgical simulations using deepfake technology, enhancing their practical skills in a controlled environment. This immersive approach bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience.
- Advancements in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
As augmented and virtual reality technologies continue to evolve, deepfakes can contribute to more immersive and realistic experiences. By integrating deepfake technology, AR and VR applications can provide users with lifelike avatars and simulations, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.

Deepfakes can be employed to create realistic virtual tour guides, historical reenactments, or language immersion experiences in virtual environments. This can greatly enhance the educational and entertainment value of AR and VR applications, making them more accessible and enjoyable for a broader audience.
For Example: In a VR tour of historical sites, deepfake technology could bring historical figures to life, guiding users through immersive experiences. Explore ancient civilizations with a virtual guide that looks, talks, and acts like a historical figure.
- Healthcare Applications:
Deepfake technology holds promise in the healthcare industry for a range of applications. Medical professionals can use realistic simulations for training purposes, allowing them to practice complex procedures in a risk-free virtual environment. Additionally, deepfakes can aid in patient education by creating personalised health information materials with lifelike explanations of medical conditions and treatment options.
For Example: In diagnostic imaging, deepfake algorithms can enhance the resolution and clarity of medical scans, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses. This application of deepfakes could contribute to advancements in medical research and the development of innovative healthcare solutions.
Medical professionals can practice complex procedures in a risk-free virtual environment, thanks to deepfake simulations. Patients could receive personalised health information with detailed, lifelike explanations of medical conditions and treatment options.
For individuals undergoing mental health therapy, deepfakes could play a role in creating virtual support groups or sessions with AI-driven therapists. This could help address issues related to accessibility, providing mental health resources to those who may face barriers to traditional therapy. Imagine a rehabilitation program that utilises realistic scenarios to help patients regain motor skills or cognitive functions in a controlled environment.
- Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention:
While deepfakes have been associated with creating synthetic content, the same technology can be harnessed for cybersecurity purposes. Deepfake detection tools are being developed to identify and prevent the spread of maliciously created content. By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms, these tools can analyse subtle inconsistencies in facial expressions, audio patterns, and other characteristics to determine if a video or audio clip is authentic.
As deepfake technology evolves, so do the countermeasures, leading to a cat-and-mouse game between creators and detectors. This ongoing development in cybersecurity can contribute to a safer digital environment by staying one step ahead of potential threats.
For Example: Deepfake detection tools can analyze subtle inconsistencies in facial expressions and audio patterns to identify authentic content. This proactive approach in cybersecurity aims to stay ahead of potential threats, creating a safer digital environment. Microsoft, for instance, has worked on solutions to identify manipulated content and deepfakes to enhance online security.

- Personalized Marketing and Advertising:
In the realm of marketing and advertising, deepfakes can be employed to create highly personalised and targeted content. Brands can use the technology to tailor advertisements to specific demographics, incorporating familiar faces and voices to establish a more relatable connection with consumers. This personalized approach has the potential to significantly improve the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, as consumers are more likely to engage with content that feels relevant and authentic to them.
By harnessing the power of deepfakes in marketing, businesses can explore innovative ways to connect with their audience, creating a more immersive and customised brand experience.
For Example: Brands can leverage deepfakes to create highly personalized advertisements. Consider an advertisement where a familiar celebrity endorses a product tailored specifically to the demographic preferences of the target audience. This personalized approach can significantly enhance the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
An advertising campaign by a beverage company used deepfake technology to show a famous actor endorsing their product in a context that appeared authentic. This raised discussions about the ethical use of deepfakes in advertising.

- Virtual Influencers and Brand Ambassadors:
Deepfake technology has given rise to the creation of virtual influencers – computer-generated personalities that can be used for marketing and brand representation. These virtual entities can be designed to embody specific characteristics and values that align with a brand’s identity. This innovative approach not only opens new creative possibilities for brand storytelling but also allows businesses to maintain full control over the virtual ambassador’s image and messaging.
For Example: Companies can design virtual influencers with specific characteristics and values to represent their brand. These digital personalities can engage with audiences on social media, endorse products, and participate in marketing campaigns. Imagine a virtual brand ambassador conducting interviews, attending events, and seamlessly blending into the online world. One well-known example is Lil Miquela, a virtual influencer involved in fashion and lifestyle.

Role of Critical Future in pioneering Deepfake Technology:
In the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence and deepfake technology, Critical Future emerges as a pioneering force, dedicated to harnessing the potential of deepfake technology for positive impact. With a focus on ethical and responsible development, Critical Future has successfully developed both video synthesis and voice cloning capabilities tailored for applications in ecommerce, education, and various other sectors. Critical Future is at the forefront of innovating “deepfake technology for good.” Their advancements in video synthesis and voice cloning open new avenues for transformative applications in ecommerce, education, and beyond. For further information or inquiries, please contact Critical Future at info@criticalfuture.co.uk.
Ethical Standards and Responsible AI:
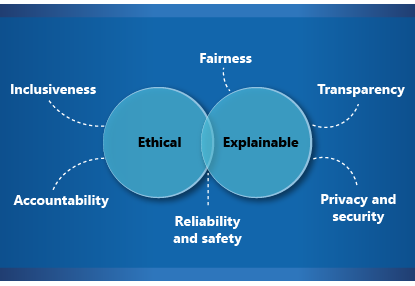
In compliance with the UK’s new AI regulation, Critical Future is dedicated to embodying key principles for ethical AI development. These include ensuring transparency, upholding fairness, implementing robust accountability and governance measures, and providing avenues for contesting AI decisions. These principles form the foundation of Critical Future’s commitment to responsible AI development, aiming to shape a future where technology aligns with human values and societal well-being. Committed to ethical practices, Critical Future places a strong emphasis on responsible AI development. Our company ensures that the technology serves as a positive force for innovation while adhering to the highest ethical standards. By prioritising these ethical standards, we not only create advanced AI systems but also contribute to a future where technology benefits everyone.
Conclusion:
In closing, deepfake technology forms a dynamic tapestry, influencing entertainment, education, and healthcare. While ethical concerns demand attention, it’s vital to appreciate the positive impact. Deepfakes revolutionise storytelling, democratise content creation, and enrich learning experiences. They contribute to cultural exchange, language learning, and historical preservation. In healthcare, deepfakes enhance patient outcomes and accessibility. The fusion with augmented reality, virtual reality, and gaming promises realistic and inclusive digital experiences. Virtual influencers redefine marketing, and deepfake art pushes the boundaries of creativity. In a rapidly advancing society, deepfakes offer a spectrum of opportunities for positive transformation.
As we navigate this complex landscape, it is imperative to approach deepfake technology with a balanced perspective—one that acknowledges both its potential benefits and the ethical challenges it poses. Responsible use, transparent regulations, and ongoing research are essential to harness the positive aspects of deepfakes while mitigating potential risks.
As we move forward, the role of Critical Future in the responsible development of deepfake technology becomes increasingly crucial. The principles outlined in the UK’s new AI regulation serve as our guiding light, shaping a responsible approach to technology development. Transparency and explainability are not mere buzzwords for us; they are the cornerstones of our commitment to ensuring that AI aligns with human values. Adhering to these ethical standards is not just a choice; it is an imperative. As technology continues to shape our world, Critical Future is dedicated to ensuring that the impact is positive, ethical, and aligned with the well-being of society at large. By fostering a collaborative and informed dialogue, we can ensure that this innovative tool becomes a force for positive change in our ever-evolving digital world.

